Resilient Cyber Newsletter #67
Cyber Information Sharing Act Lapse, White House Continues AI Deregulatory Push, MCP Malware Wave, AI Security Shared Responsibility Model, AI Code Generation Challenges & Time-to-Exploit Acceleration
Welcome!
Welcome to issue #67 of the Resilient Cyber Newsletter.
It’s been an interesting week, marked by continued challenges in AI coding, the growth of MCP malware, and the acceleration of vulnerability exploitation, all against a backdrop of a U.S. government shutdown and the lapse of key cybersecurity provisions and activities. So, let’s take a look and see where we stand as an industry for the week!
SANS Difference Makers Awards!
Before we get going, I wanted to mention that Resilient Cyber has been nominated for the 2025 SANS Difference Makers Awards, specifically in the Media Creator Category. If you enjoy the content I put so much effort into at Resilient Cyber for the community, I would truly appreciate if you would go cast a vote for me.
Interested in sponsoring an issue of Resilient Cyber?
This includes reaching over 40,000 subscribers, ranging from Developers, Engineers, Architects, CISO’s/Security Leaders and Business Executives
Reach out below!
Stop Social Engineering at the Source - Live Webinar
Cyber adversaries don’t need zero-days—they need your people. In this joint webinar from DeleteMe, SocialProof Security, and GuidePoint Security, experts Rachel Tobac, Victor Wieczorek, and Glen Sorensen will show how exposed personal data fuels doxxing, impersonation, and phishing campaigns.
Learn how attackers map OSINT into compromise, and the strategies security teams are using to reduce executive and employee risk at scale. Walk away with a playbook for shrinking your human attack surface.
Cyber Leadership & Market Dynamics
AI Engineer Equity Rockets Higher
We’ve heard a lot about the battle for AI talent and seen the headlines out of OpenAI, Meta, and others, but the trend isn’t isolated to the giants either. A recent post by Peter Walker of Carta highlighted how startups are offering massive equity packages in an effort to attract top AI engineering talent.
Peter summarized key points, such as the average salary increase for AI engineers of 9% over 18 months, which is three times the average increase for other roles, while their equity packages have risen by 26%.
Peter teased that the trend could continue, impacting remaining equity pools for other roles, or we could see a bubble pop and deflation.
If you’re in cyber and thinking, "What do I care?" Step back and realize that AI security is a related field, and developing deep domain expertise in securing AI could also serve you well.
U.S. Government Scrambles to Stop New Hacking Campaign Blamed on China
Government officials are warning that Chinese hackers have been able to persist inside government networks since May by exploiting vulnerable and unpatched Cisco security gear deployed across U.S. government networks.
This came to a head via a recent emergency directive from CISA this past Thursday, which ordered all civilian agencies to test their Cisco firewall equipment to see if it has been breached. CISA ordered agencies to disconnect devices that have been compromised immediately and also stated that several of these devices are deployed across U.S. critical infrastructure.
We continue to see the targeting of both U.S. critical infrastructure by malicious foreign actors, often lying dormant for potential future malicious use. We also continue to see hackers targeting security vendors and products, which is a topic I discussed at length in my article titled “Your Security Tools May Be Making You Insecure”.
Vital Cyber Data-Sharing Law Appears Likely to Expire Amid Looming Government Shutdown
The 2015 Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act allows private sector providers to transmit cyber threat intelligence to government partners, providing key legal protections, including immunity from lawsuits and regulatory penalties when sharing threat data.
The law is set to lapse by September 30th unless it gets renewed by Congress, which seems unlikely given the timeline of my writing this. Many have tried to raise the alarm about this, but Congress thus far hasn’t acted. Many argue that a lapse in the law will prevent entities from sharing threat information and hinder their ability to respond to emerging threats.
Israeli Tech Raises $11.9B in 2025 as M&A Soars to $71B, 5x Last Year
Last week, I shared the State of Israeli Cyber M&A from Dorin of VC firm Nightdragon. This recent Ctech piece highlights how Israeli tech M&A has been massive in 2025, 5x the amount from 2024.
As anyone who follows the cybersecurity market knows, Israel is a dominant force in the ecosystem; these numbers are impressive, but they also represent the strength of its tech and cyber industries.
Cybersecurity Incidents and Government Bailouts
I’ve come across discussions about the concept of a cybersecurity backdrop/insurance that the Government backs. Still, this case, from outside the UK, is one of the first I can recall where the Government stepped in with a loan guarantee.
It was recently announced that the UK Government provided Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) with a $1.5 billion loan guarantee to help restore its supply chain after a cyberattack caused production to halt. The UK government cited the incident as not only an attack on JLR but the UK’s automotive industry as a whole. This is a fascinating example where Governments may be forced to subsidize and bail out private organizations that are critical to their economies and labor markets, and I could see this happening in many other places, including in the U.S., in time.
Netskope Slumps Post-IPO
As many are aware, Netskope broke somewhat of an IPO impasse among cyber recently, but what I found interesting from Zeus Kerravala is their stock has since dipped post-IPO. As he points out, some analysts are speculating the company is “losing too much money”, based on the rule of 40, since their growth is 31% but their operating margin is -28% for a number of “3”.
Compared to their peers:
Zscaler - 53.5%
Palo Alto Networks - 52.5%
Crowdstrike - 49.0%
Cloudflare - 38.4%
Oneleet Announces $33M Series A
Cybersecurity startup Oneleet announced its $33M Series A, led by Dawn Capital. Their CEO Bryan Onel tool to social media to announce that they’re aiming to end compliance theater and are getting companies compliant with frameworks such as SOC2, ISO 27001, etc. in short order while also making companies secure, and allowing them to consolidate vendors/tools such as pen testing, code scanning, CSPM, MDM and more into an integrated platform (note the platform play emphasis). Bryan also mentioned they have grown to 8-figure revenue profitability without even touching their seed funding - all organic.
AI
White House Continues AI De-Regulatory Push
While others, such as the EU, are ramping up AI regulation efforts, here in the U.S., the current administration is continuing its push to deregulate AI and position the U.S. as a world leader of this critical technology by minimizing regulations and impediments.
On September 26th, the White House issued an RFI seeking input from the public on any Federal laws, rules, and policies that “unnecessarily hinder” the development or deployment of AI.
This ties to earlier presidential goals, such as the release of “Winning the Race: America’s AI Action Plan”.
Agentic AI Security Landscape - Q2/3 2025
OWASP’s GenAI Security Project produced an “Agentic AI Security Landscape” update for the final quarters of 2025. The landscape cheat sheet breaks vendors down across key categories and activities: Govern, Monitor, Augment & Fine-Tune Data, T&E, Release, Deploy, and Operate.
You’ll notice many familiar faces in the landscape, including AI security leaders who have been in the headlines via acquisition and startups that are providing unique and differentiating capabilities.
OpenAI and NVIDIA Announce Strategic Partnership
The AI industry leaders recently announced a strategic partnership to deploy 10 gigawatts of AI data centers, which is millions of GPUs from NVIDIA, to power OpenAI. This involves an investment of up to $100 billion from NVIDIA in OpenAI, with the first gigawatt of NVIDIA systems anticipated to be deployed in the second half of 2026.
Prompt Injection - and a $5 domain - trick Salesforce Agentforce into leaking sales
By now, we’re used to seeing prompt injection vulnerabilities/attacks against AI systems. The latest example came from Salesforce’s Agentforce, where a now-fixed flaw could have allowed attackers to steal sensitive customer data.
For those unfamiliar, Agentforce is Salesforce’s tool that enables users to automate tasks with AI agents; however, this vulnerability would have allowed the AI agents to retrieve CRM records and send them to an external source.
MCP Malware Wave 🌊
It was discovered by Noma Security and dubbed “ForcedLeak”. The method used by Noma here was also interesting, involving an expired domain and utilizing indirect prompt injection in a description field within the CRM system.
I continue to be impressed with the awesome research the team at Koi is doing. In short order, this past week, they discovered the first malicious MCP server targeting developers.
Then, today, they announced that they discovered a fully functional MCP server that has been weaponized with a hidden backdoor, which had hundreds of installs during the period of weaponization.
This includes creating an immediate reverse shell to the attacker's server upon installation, and a second upon activation that consists of a hidden interactive shell with a persistent TCP connection to the attacker’s server, providing them with remote access.
Much like open source, developers and organizations are haphazardly downloading and running publicly available MCP servers, which compromises them.
Tony Turner and I published the software supply chain book “Software Transparency” with Wiley in 2023, where we discussed these pull-style attacks on open source - never knowing at the time that the rise of GenAI, LLMs, and Agents would continue to add novelty to the attack landscape.
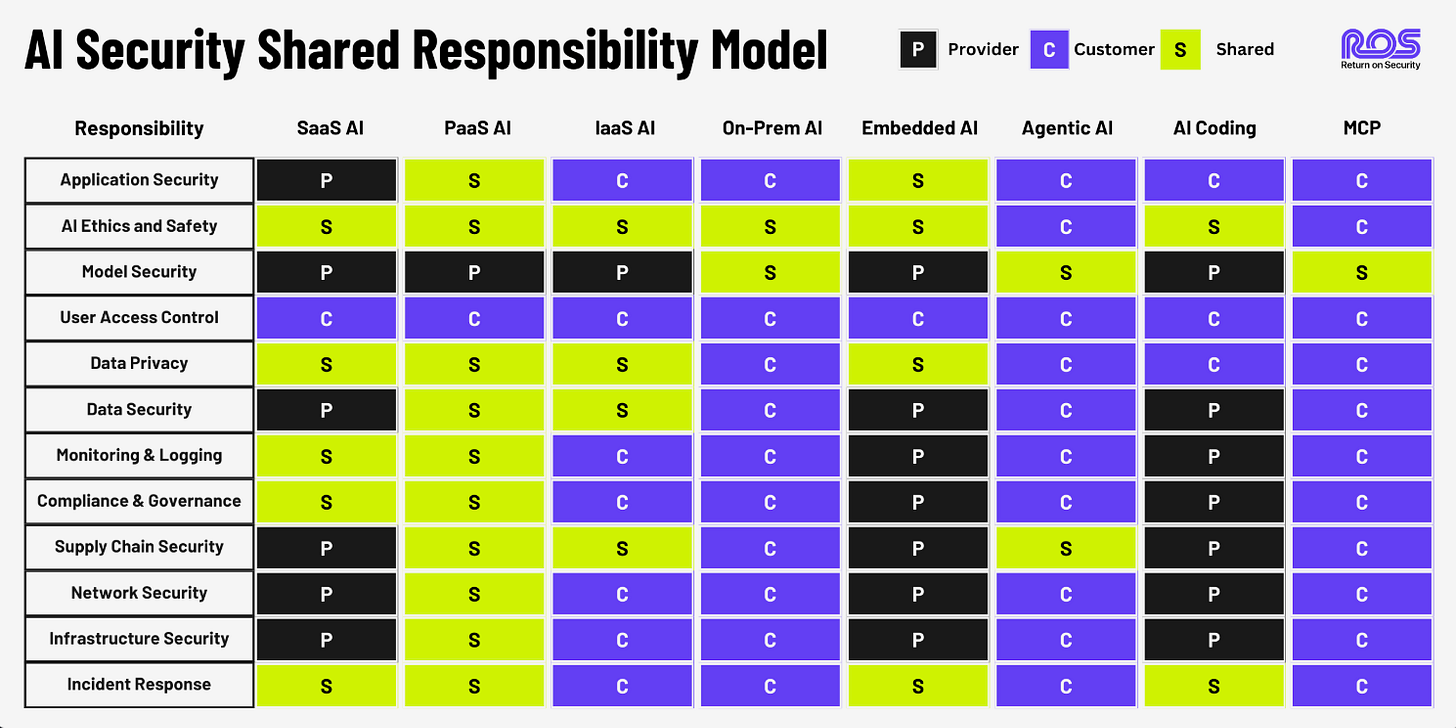
(Updated) AI Security Shared Responsibility Model
Earlier this year, I shared the AI Security Shared Responsibility Model from my friend Mike Privette over at Return on Security (RoS). Mike recently released an updated version of the model, including key changes.
This is an excellent resource for the community and is similar to the widely cited cloud shared responsibility model, but accounts for nuanced aspects of AI consumption and usage.
It includes:
8 Deployment Models
16 Security Domains
Responsibility Matrix
California Governor Signs Landmark AI Safety Bill
While we have seen a pause in federal AI regulation, and even a push to deregulate AI at the U.S. Federal level, states continue to move forward with their own regulations. Notably, California recently signed its landmark AI safety bill into law.
It requires large AI labs (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta, and DeepMind) to be transparent about their safety protocols and to provide whistleblower protections for employees within these companies.
AppSec
Implications of Over-Reliance on CLIs vs. IDEs?
Industry leader and investor Chenxi Wang posted a thought-provoking piece this week, examining the rise of CLIs, as seen in leading tools such as Gemini, Claude, and GitHub, where developers are working more and more in the CLI and less and less in the IDE.
As she mentioned, this means developers spending time reading a diff of changes, auditing changes, and deciding whether to accept or reject code, but could lead to less time in the actual code, familiarity with the codebase and applications, and opportunities to miss bugs, security flaws, a mental map of the overall system, and becoming over-reliant on AI suggestions.
This is something some reports already show, with some studies saying AI reliance can lead to cognitive decline in terms of usage, and also a tendency to “trust” the AI without rigorous review.
Security Degradation in Iterative AI Code Generation
We are aware that widespread adoption of LLM and AI coding is underway. That said, the security implications of this are still evolving, and researchers continue to look into what these trends may mean for the digital attack surface.
I came across a paper I hadn’t seen yet, which was initially released in June of 2025, but updated in September, and it has some interesting and concerning findings. It involves 400 code samples across 40 rounds of “improvements” using four different prompting strategies, and it found the code actually got WORSE, not better, in terms of critical vulnerabilities. In fact, after five iterations of “improvements,” the critical vulnerability count went up by nearly 40%.
-1 Days 😳
This week, I came across a post from Brent Muir who shared an insight from Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG). They examined the average time to exploitation (TTE) of vulnerabilities from the time a patch is disseminated.
The shocking part?
In 2024, it was -1 days.
Yes, you’re reading that right. On average, across the 112 samples, the exploitation of the vulnerabilities examined was less than a day. This demonstrates that malicious actors are now, on average, exploiting vulnerabilities before a patch is even created and widely available.
This emphasis on zero-day exploitation highlights several key points to me right off the bat.
Organizations absolutely should be practicing defense in depth and having compensating/mitigating controls in place, as they’re being exploited before patching is even an option
As I said above, we hear “patch, patch, patch!” And of course, this is valid, but as demonstrated, sometimes patching isn’t an option even if you were somehow an outlier who patches everything in a day or less of availability
Choose your vendors and products wisely. Do vendors routinely disclose new zero-day/critical vulnerabilities? May want to take a look at that and consider other options. That said, a lack of vulnerability disclosure also doesn’t imply things are secure either…
Minimize your attack surface.
Patching is problematic, and nearly all sizable organizations struggle to maintain tight remediation SLAs they can adhere to. This means minimizing unnecessary dependencies, shelfware, products, and systems that aren’t necessary, among other things.
Everything is ripe for exploitation.
Time from CVE Disclosure to Known Exploitation
While the above share from Google went viral via my LinkedIn feed, Vulnerability Researcher and friend Patrick Garrity stepped in to be a voice of reason, too. He shared that throughout 2025, less than a third of known exploited vulnerabilities were zero-day vulnerabilities, despite the catchy image from Google.
GitHub Announces Revocation API Generally Available
In the wake of several high-profile incidents, including those impacting npm, GitHub recently announced the general availability of its credential revocation API, which can help accelerate the revocation of exposed privileged access tokens (PATs).