Entering the AI Controls Matrix
A look at Cloud Security Alliance's AI Controls Matrix
If you’re following the cybersecurity space, you inevitably have noticed that topics such as AI governance and secure adoption are a core part of the AI conversation. We see different approaches to AI regulation, such as in the U.S. or the EU, and frameworks from ISO and NIST to help organizations securely govern and implement AI.
Not to be left behind, the Cloud Security Alliance recently launched its “AI Controls Matrix: A Comprehensive Framework for Trustworthy AI,” and I wanted to check it out and share my findings with you all.
So, let’s take a look.
Interested in sponsoring an issue of Resilient Cyber?
This includes reaching over 45,000 subscribers, ranging from Developers, Engineers, Architects, CISO’s/Security Leaders and Business Executives
Reach out below!
High-Level
At a high level, CSA:
“Envisions organizations using the AI Controls Matrix (AICM) to develop, implement, and operate AI technologies in a secure and responsible manner.”
Thankfully, CSA didn’t set out to reinvent the wheel and instead leaned into some of the resources I mentioned above, such as ISO 42001, ISO 27001, NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), and BSI.
It is also a freely available resource to the community, developed by leading AI and security professionals through collaborative input. It is vendor-agnostic and not tied to any specific AI product, platform, or provider.
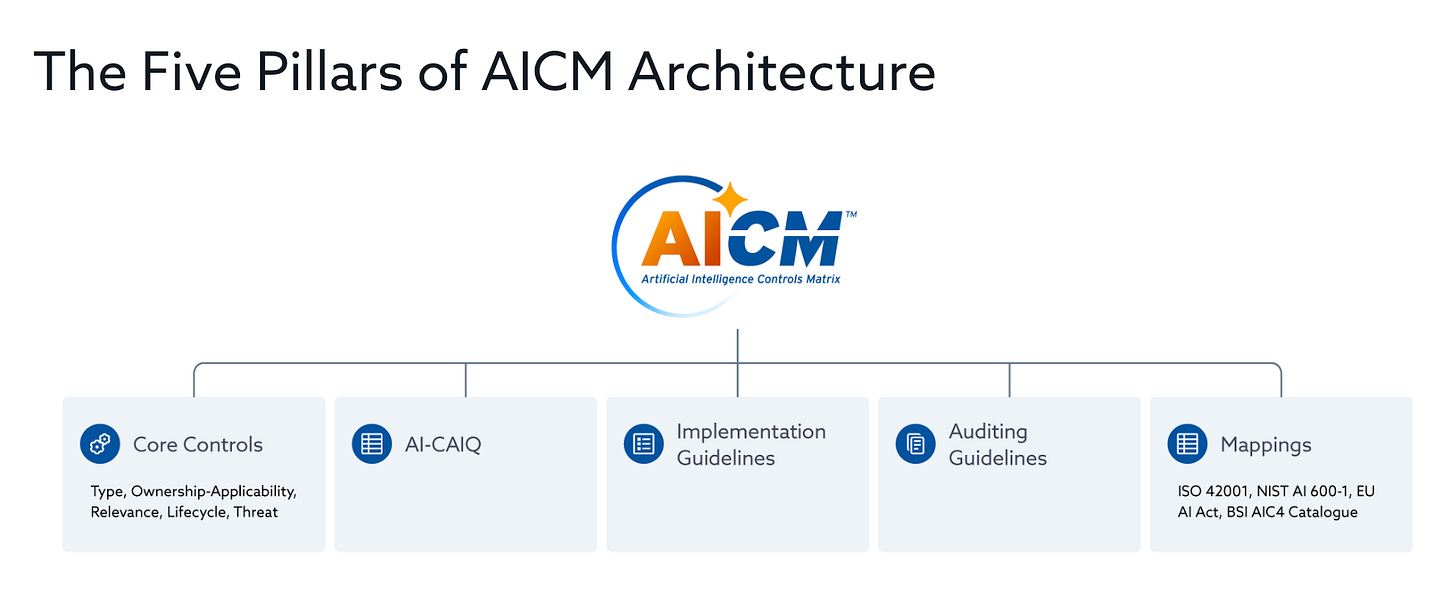
The AICM has five pillars, which are seen below:
Each control covers factors such as:
Control Type
Control Applicability and Ownership
Architectural Relevance
Lifecycle Relevance
Threat Category
The CSA also released a presentation introducing AICM:
At the AICM landing page you can download an “AICM Bundle”, which I did, and it includes an AI-CAIQ of AICM (Questionnaire), mappings of AICM to BSI AI C4 and AICM to NIST 600-1, as well as AICSM v 1.0 itself.
AICM includes 243 controls structured across 18 domains.
When you open AICM you can see the various taps, such as Introduction, AICM v1, Scope Applicability, AICM Self-Assessment Questions, and more.
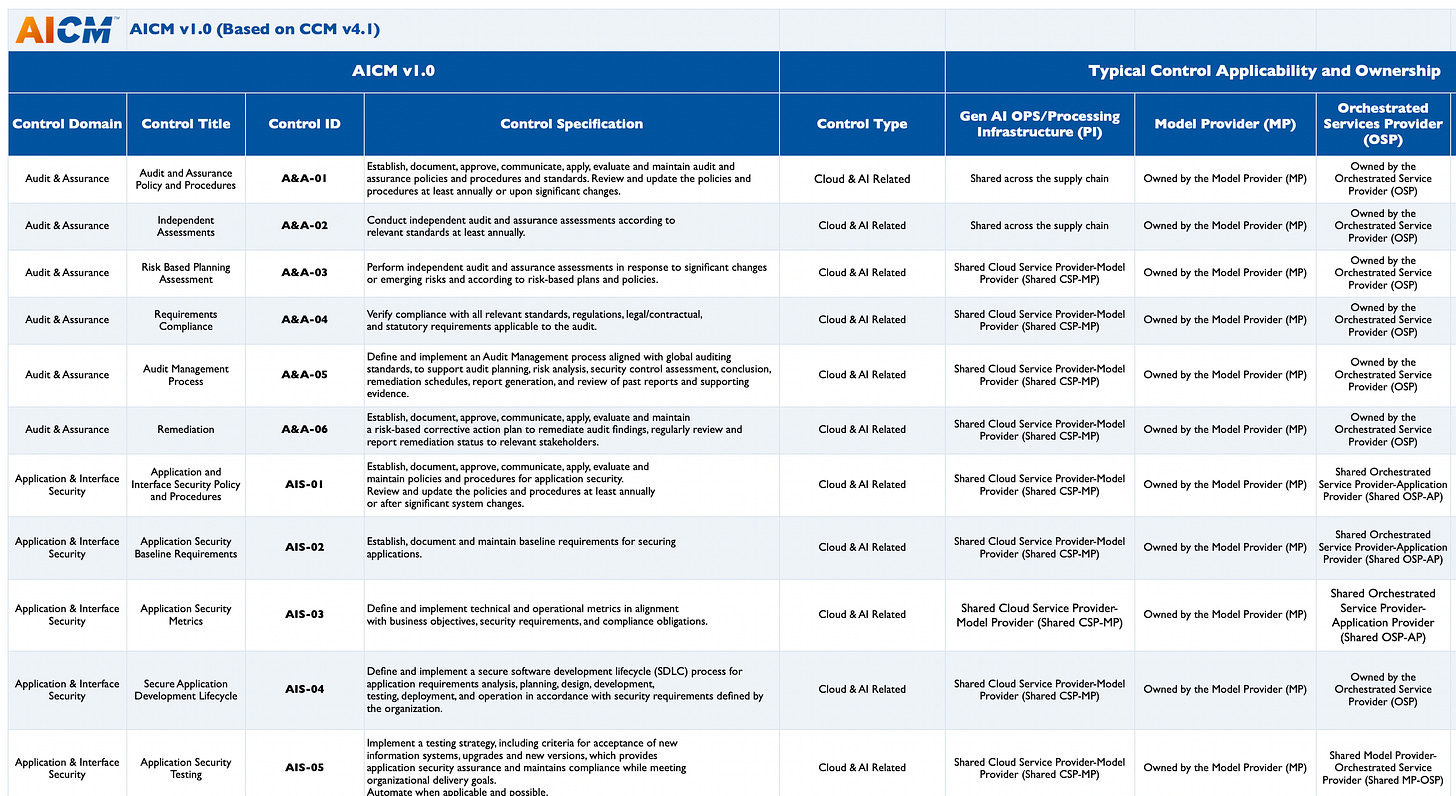
Below is a snapshot, where you can see Control Domains, Titles, ID’s, Specifications, Type and more. You can see how some controls are Cloud & AI Related, while others are strictly AI Related.
Additionally, they help break down the typical control applicability and ownership, with some being owned by the model provider whereas others for example may be shared by the owned by the AI customer and some are shared, much like the Cloud Shared Responsibility Model prior to AI’s widespread adoption.
AICM Scope/Mapping
Another tab in the AICM sheet is the AICM Scope Applicability (Mapping) tab, which is helpful if you’re organization has or will need to align with and implement other frameworks such as BSI AI C4, NIST AI RMF etc.
It lays out what AICM controls have no gaps with mapping to other frameworks, and which ones either are a full or partial gap, as you crosswalk your compliance and alignment across the various frameworks.
AICM Control Domains
Personally whenever I see a new control framework, I like to get a look at the control domains that it involves, to understand how it groups controls as well as what the scope of the overall framework is. Let’s take a look at the Control Domains from AICM
Audit And Assurance
Application and Interface Security
Business Continuity Management and Operational Resilience
Change Control and Configuration Management
Cryptography, Encryption and Key Management
Datacenter Security
Data Security and Privacy Lifecycle Management
Governance, Risk and Compliance
Human Resources
IAM
Interoperability and Portability
Infrastructure Security
Logging and Monitoring
Model Security
Security Incident Management, E-Discovery & Cloud Forensics
Supply Chain Management, Transparency and Accountability
Threat & Vulnerability Management
Universal Endpoint Management
As you can see, the AICM Control Domains are both robust and diverse, covering a combination of people, process and technology, as well as both underlying infrastructure and core application security concepts while also accounting for novel aspects of AI, such as Model Security.
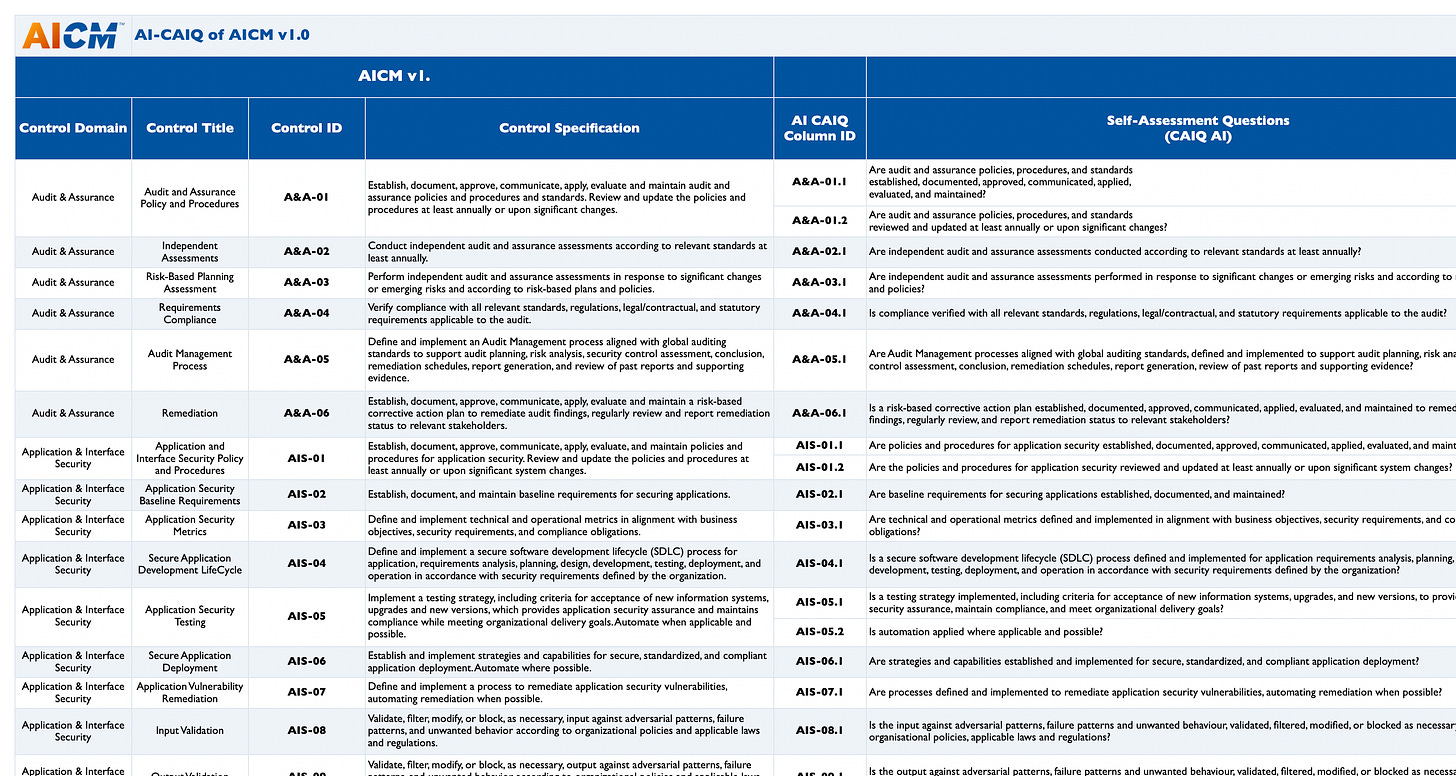
AICM Self-Assessment Questions
The AICM Self-Assessment Question tab is helpful as it lays out the controls discussed above and provides a library of self-assessment questions so organizations can conduct self-assessments to identify where they are meeting AICM controls (and controls in the other frameworks it maps to) and where they gave gaps they need to document and remediate at a future date.
LLM Taxonomy
The LLM Taxonomy is also helpful as much of the lexicon around LLMs and AI may be new to organizations, security practitioners and the assessment and audit community. Phrases such as Retreival-Augmented Generation (RAG), Fine-Tuning, Data Poisoning, Model Manipulation and more.
Tying It All Together
AICM represents another great contribution to the Cyber community from CSA and ties into the CSA ecosystem of other resources as well. For example, they shared they launched their “STAR for AI Program” where organizations can demonstrate a commitment to trustworthy AI and even achieve a third-party validation of organizational alignment with AICM. They also offer an AI Trustworthy Pledge organizations can make.
While not currently required by regulatory frameworks and regimes, AICM represents a robust and coherent approach to helping organizations implement AI securely and a repeatable and scalable way for assessors to measure that. It’s ability to tie together the various leading frameworks from a mapping perspective also makes it a great resource for organizations to measure their maturity across leading AI frameworks in an effective manner.
Great work by the entire AICM and CSA teams who contributed to this resource for the community!





Just downloaded today, thanks for the write up!